UIC dataset
- Citation Author(s):
-
Uzapi Hange (Wuhan university of technology)Ezenwa Chike Nwanesi (Yanshan university)Monhesea Obrey Patrick Bah (Wuhan university of technology)
- Submitted by:
- Uzapi Hange
- Last updated:
- DOI:
- 10.21227/7zec-8827
- Data Format:
 3 views
3 views
- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
The dataset was constructed based on the World Economic Forum's Global Competitive Index (GCI) historical dataset. The data collected is anchored on four main pillars that influence university-industry collaboration performance (UIC): Higher learning and research institutes (pillar I), Government involvement (pillar II), Resources (pillar III), and Absorptive capacity (pillar IV). The dataset records 21 indicators of over 140 countries on 4 pillars of university-industry collaboration performance between 2007 and 2017.
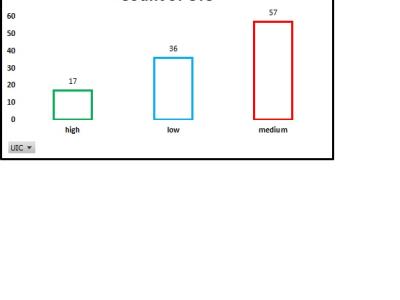
The “UIC performance” measured using a scale of 1-7, 1 being the worst and 7 being the best, was used as a baseline for coding the class attribute (UIC). A UIC performance score below 3 was coded as “low”, a score between 3 and 5 was coded as “medium”, while any score above 5 was coded as “high”.
Instructions:
Data understanding
- Time Coverage: The dataset records 21 indicators of over 140 countries on 4 pillars of university-industry collaboration performance between 2007 and 2017.
- Key variables are grouped into four pillars. Pillar I: Higher learning and research institutes: This pillar is made up of 7 items (Tertiary education enrolment, Higher education and training, Quality of the education system, Quality of scientific research institutions, Quality of math and science education, Quantity of education, and Quality of education). Pillar II: Government Involvement: This pillar consists of 4 items (Government spending, Burden of government regulation, Transparency of government policy-making and Ease of access to loans). Pillar III: Resources: This pillar has 7 items (Availability of scientists and engineers, Extent of staff training, Efficient use of talent, ICT use, Infrastructure, Availability of the latest technologies and Availability of research and training services). Pillar IV: Absorptive Capacity: This pillar is made up of 3 items (Company spending on R&D, Firm-level technology absorption and Capacity for innovation).
Data preprocessing
- Open the dataset using Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, or any other data analysis software.
- Import the dataset in Python/R/SPSS for advanced statistical analysis.
- Check for missing data, class imbalance and confirm the data types.
Key Insights
- University-industry collaboration performance trends:Identify annual peaks and declines in performance.
- Government Involvement Effectiveness: Analyze how government policies and their involvements impacted the university-industry collaboration score (low, medium, or high).
- Resource Effectiveness: Analyze how the availability of specialized resources has impacted the university-industry collaboration score.
- Absorptive capacity Impact: Analyze how Absorptive Capacity has impacted the university-industry collaboration score.
- University-industry collaboration performance prediction: Use machine learning models to predict future university-industry collaboration performance (low, medium, or high).
Uses for Researchers & Data Scientists
- Conduct statistical analysis to understand University-industry collaboration trends.
- Apply feature selection techniques identifying the most prominent features impacting university-industry collaboration performance.
- Apply machine learning models for university-industry collaboration performance classification.
- Apply structural equation modeling to analyze the interdependencies between the pillars and their mediation role in university-industry collaboration performance.
Uses for industry players
- Effectively identify high/low-performing collaborations and partners based on prediction models.
- Develop informed resource allocation strategies.
- Identify their absorptive capacity levels and subsequently develop strategies on how to enhance them.
Uses for universities and research institutes
- Effectively identify high/low-performing collaborations and partners based on prediction models.
- Develop informed resource allocation strategies.
- Develop courses that align with industry needs.
- Develop strategies for enhancing research commercialization.
Uses for policy makers
- Analyze the effectiveness of government policies on the university-industry collaboration success.
- Effectively identify high/low-performing collaborations and develop policies that facilitate successful collaborations.
- Develop informed resource allocation strategies.







