SensorNetGuard: A Dataset for Identifying Malicious Sensor Nodes

- Citation Author(s):
-
Dr Karthick Raghunath K MDr Arvind K S
- Submitted by:
- K M Karthick Raghunath
- Last updated:
- DOI:
- 10.21227/ba0m-cy61
- Data Format:
- Links:
 2287 views
2287 views
- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
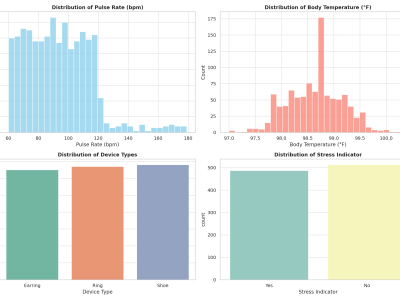
The dataset, titled "SensorNetGuard: A Dataset for Identifying Malicious Sensor Nodes," comprises 10,000 samples with 21 features. It is designed to facilitate the identification of malicious sensor nodes in a network environment, specifically focusing on IoT-based sensor networks.
General Metrics
§ Node ID: The unique identifier for each node.
§ Timestamp: The time at which data or a packet is sent or received.
§ IP Address: Internet Protocol address of the node.
Network Traffic Metrics
§ Packet Rate: The number of packets sent/received per unit time.
§ Packet Drop Rate: The rate at which packets are being dropped.
§ Packet Duplication Rate: The rate at which packets are duplicated.
§ Data Throughput: The amount of data successfully transferred from one point to another in a given time frame.
Signal Metrics
§ Signal Strength: Measured in dBm, indicates the power level of the signal.
§ Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR): Measures the clarity of the signal.
Power Usage Metrics
§ Battery Level: Remaining power in the node.
§ Energy Consumption Rate: The rate at which the node consumes energy.
Routing Metrics
§ Number of Neighbors: The count of nodes within direct communication range.
§ Route Request Frequency: The frequency with which a node is asking for routes.
§ Route Reply Frequency: The frequency with which a node responds to route requests.
Behavioral Metrics
§ Data Transmission Frequency: How often a node sends data.
§ Data Reception Frequency: How often a node receives data.
§ Error Rate: The number of erroneous packets per unit time.
Miscellaneous Metrics
§ CPU Usage: The percentage of CPU being used by the node.
§ Memory Usage: The amount of RAM being used.
§ Bandwidth: Available data transmission rate.
Metrics Specific to Attacks
§ Is_Malicious: A binary flag (0 or 1) indicating whether the node is malicious.
The dataset includes a diverse range of features that allow for the application of machine learning models to identify various types of attacks, such as black hole, gray hole, flooding attacks, and Sybil attacks. Some features may be more relevant for specific types of attacks, so feature engineering and selection are crucial steps. Various machine learning algorithms can be trained on this dataset. The "Is_Malicious" column serves as the ground truth for learning algorithm. For unsupervised learning, anomaly detection algorithms can be used to identify outliers or anomalies that may correspond to malicious activities.
Being able to accurately identify malicious nodes can significantly improve the security posture of sensor networks, particularly in IoT environments where such attacks can have severe consequences.
By training a model on this dataset, network administrators can identify potential security threats in real-time, thus enabling proactive measures to isolate or remove malicious nodes.
Ultimately, the dataset serves as a comprehensive resource for developing and validating machine learning models aimed at enhancing network security by identifying malicious sensor nodes.
Instructions:
By training a model on this dataset, network administrators can identify potential security threats in real-time, thus enabling proactive measures to isolate or remove malicious nodes.
Ultimately, the dataset serves as a comprehensive resource for developing and validating machine learning models aimed at enhancing network security by identifying malicious sensor nodes.