Breast Invasive Carcinoma
- Citation Author(s):
-
Giovanni Ciriello (Department of Medical Genetics, University of Lausanne (UNIL), 1011 Lausanne, Switzerland)Michael L GatzaAndrew H BeckMatthew D WilkersonSuhn K RhieAlessandro PastoreHailei ZhangMichael McLellanChristina YauCyriac KandothReanne BowlbyHui ShenSikander HayatRobert FieldhouseSusan C LesterGary M K TseRachel E FactorLaura C CollinsKimberly H AllisonYunn-Yi ChenKristin JensenNicole B JohnsonSteffi OesterreichGordon B MillsAndrew D CherniackGordon RobertsonChristopher BenzChris SanderPeter W LairdKatherine A HoadleyTari A KingTCGA Research NetworkCharles M Perou
- Submitted by:
- Raktim Kumar Mondol
- Last updated:
- DOI:
- 10.21227/2wtc-wd25
- Links:
 645 views
645 views
- Categories:
Abstract
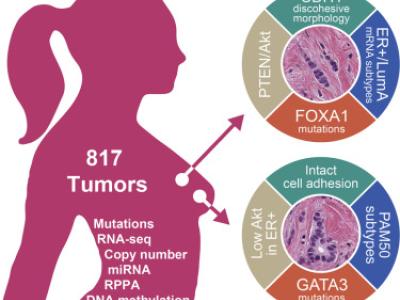
Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) is the second most prevalent histologic subtype of invasive breast cancer. Here, we comprehensively profiled 817 breast tumors, including 127 ILC, 490 ductal (IDC), and 88 mixed IDC/ILC. Besides E-cadherin loss, the best known ILC genetic hallmark, we identified mutations targeting PTEN, TBX3 and FOXA1 as ILC enriched features. PTEN loss associated with increased AKT phosphorylation, which was highest in ILC among all breast cancer subtypes. Spatially clustered FOXA1 mutations correlated with increased FOXA1 expression and activity. Conversely, GATA3 mutations and high expression characterized Luminal A IDC, suggesting differential modulation of ER activity in ILC and IDC. Proliferation and immune-related signatures determined three ILC transcriptional subtypes associated with survival differences. Mixed IDC/ILC cases were molecularly classified as ILC-like and IDC-like revealing no true hybrid features. This multidimensional molecular atlas sheds new light on the genetic bases of ILC and provides potential clinical options.