Dataset Entries from this Author

Most machine learning (ML) proposals in the Internet of Things (IoT) space are designed and evaluated on pre-processed datasets, where the data acquisition and cleaning steps are often considered a black box. Therefore, the data acquisition stage requires additional data cleaning/anomaly techniques, which translate to additional resources, energy, and storage.
- Categories:
Open Access Entries from this Author

We introduce a dataset concerning electric-power consumption-related features registed in seven main municipalities of Nariño, Colombia, from 2010 to 2016. The dataset consists of 4423 socio-demographic characteristics, and 6 power-consumption-referred measured values. Data were fully collected by the company Centrales Eléctricas de Nariño (CEDNEAR) according to the client consumption records.
- Categories:
Category
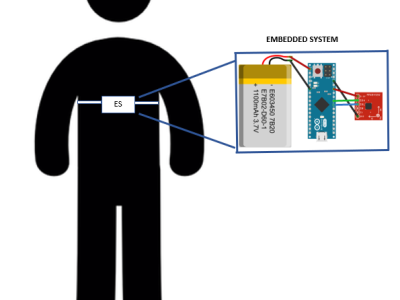
The electronic system has been design to know the position human body. Of this way the system use a three axis accelerometer to detect five common positions (i) ventral decubitus, (ii) right lateral decubitus, (iii) left lateral decubitus, (iv) supine decubitus and (v) seated. The sensor data was acquire with ten diferrents persons, their each positions was how they felt confortable. The accelerometer acquire data from 3 axis possible (X,Y,Z)
- Categories:
Category
S1= Preasure sensor, value 0-1023 decimalS2= Preasure sensor, value 0-1023 decimalS3= Preasure sensor, value 0-1023 decimalS4= Ultrasonic sensor, value 0-15 cm
- Categories:
Category
