Raw data used in the manuscript "The use of mixed collagen-Matrigel matrices of increasing complexity recapitulates the biphasic role of cell adhesion in cancer cell migration: ECM sensing, remodeling and forces at the leading edge of cancer invasion"
- Citation Author(s):
-
María Anguiano (IDISNA, Ciberonc and Solid Tumours and Biomarkers Program, Center for Applied Medical Research, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain)Xabier Morales (IDISNA, Ciberonc and Solid Tumours and Biomarkers Program, Center for Applied Medical Research, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain)Carlos Castilla (IDISNA, Ciberonc and Solid Tumours and Biomarkers Program, Center for Applied Medical Research, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain)Alejandro Rodríguez Pena (IDISNA, Ciberonc and Solid Tumours and Biomarkers Program, Center for Applied Medical Research, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain)Cristina Ederra (IDISNA, Ciberonc and Solid Tumours and Biomarkers Program, Center for Applied Medical Research, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain)Martín Martínez (Neuroimaging Laboratory, Division of Neurosciences, Center for Applied Medical Research, University of Navarra, 31008 Pamplona, Spain )Mikel Ariz (IDISNA, Ciberonc and Solid Tumours and Biomarkers Program, Center for Applied Medical Research, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain)Maider Esparza (IDISNA, Ciberonc and Solid Tumours and Biomarkers Program, Center for Applied Medical Research, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain)Hippolyte Amaveda (Department of Mechanical Engineering, Multiscale in Mechanical and Biological Engineering (M2BE), Aragon Institute of Engineering Research (I3A). University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain)Mario Mora (Department of Mechanical Engineering, Multiscale in Mechanical and Biological Engineering (M2BE), Aragon Institute of Engineering Research (I3A). University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain)Nieves Movilla (Department of Mechanical Engineering, Multiscale in Mechanical and Biological Engineering (M2BE), Aragon Institute of Engineering Research (I3A). University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain)José Manuel García Aznar (Department of Mechanical Engineering, Multiscale in Mechanical and Biological Engineering (M2BE), Aragon Institute of Engineering Research (I3A). University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain)Iván Cortés-Domínguez (IDISNA, Ciberonc and Solid Tumours and Biomarkers Program, Center for Applied Medical Research, University of Navarra, Pamplona, Spain)
- Submitted by:
- Carlos Ortiz De Solorzano
- Last updated:
- DOI:
- 10.21227/va80-yf12
 374 views
374 views
- Categories:
Abstract
The migration of cancer cells is highly regulated by the biomechanical properties of their local microenvironment. Using 3D scaffolds of simple composition, several aspects of cancer cell mechanosensing (signal transduction, EMC remodeling, traction forces) have been separately analyzed in the context of cell migration. However, a combined study of these factors in 3D scaffolds that more closely resemble the complex microenvironment of the cancer ECM is still missing. Here, we present a comprehensive, quantitative analysis of the role of cell-ECM interactions in cancer cell migration within a highly physiological environment consisting of mixed Matrigel-collagen hydrogel scaffolds of increasing complexity that mimic the tumor microenvironment at the leading edge of cancer invasion. We quantitatively show that the presence of Matrigel increases hydrogel stiffness, which promotes β1 integrin expression and metalloproteinase activity in H1299 lung cancer cells. Then, we show that ECM remodeling activity causes matrix alignment and compaction that favors higher tractions exerted by the cells. However, these traction forces do not linearly translate into increased motility due to a biphasic role of cell adhesions in cell migration: at low concentration Matrigel promotes migration-effective tractions exerted through a high number of small sized focal adhesions. However, at high Matrigel concentration, traction forces are exerted through fewer, but larger focal adhesions that favor attachment yielding lower cell motility.
Instructions:
The datasets is made of a number of zip files. The name of the file identifies the figure (and figure panel) that the data refers to.
Dataset Files
- Figure2_Matrix fiber staining Table2_Quantification of matrix parameters.zip (Size: 13.97 KB)
- Figure2_Hydrogel architecture Matrix fiber staining Hydrogel_C.zip (Size: 774.27 MB)
- Figure2_Hydrogel architecture Matrix fiber staining Hydrogel_CM.zip (Size: 821.71 MB)
- Figure2_Hydrogel architecture Matrix fiber staining Hydrogel_CM+.zip (Size: 859.5 MB)
- Figure3_Hydrogel stiffness.zip (Size: 2.34 MB)
- Figure4_Cell migration throught 3D Hydrogels.zip (Size: 1.04 GB)
- Figure5_Invasion analysis throught 3D hydrogels.zip (Size: 657.91 MB)
- Figure6_Hydrogel remodelation.zip (Size: 14.98 MB)
- Figure7b-e_Hydrogel degradation images 20% FBS Hydrogel_C.zip (Size: 336.93 MB)
- Figure7b-e_Hydrogel degradation images 20% FBS Hydrogel_CM.zip (Size: 612.25 MB)
- Figure7b-e_Hydrogel degradation images 20% FBS Hydrogel_CM+.zip (Size: 786.82 MB)
- Figure7b-e_Hydrogel degradation images GM6001 Hydrogel_C.zip (Size: 276.54 MB)
- Figure7b-e_Hydrogel degradation images GM6001 Hydrogel_CM.zip (Size: 351.57 MB)
- Figure7b-e_Hydrogel degradation images GM6001 Hydrogel_CM+.zip (Size: 898.78 MB)
- Figure7a_Hydrogel degradation quantification.zip (Size: 15.02 KB)
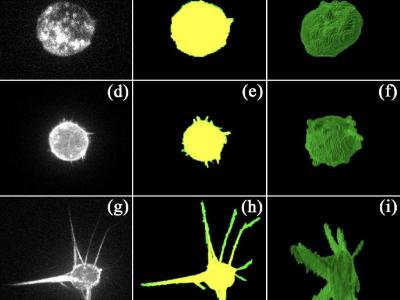
- Figure8_Focal adhesions morphology.zip (Size: 77.58 MB)
- Figure9_Integrin expression during cell migration.zip (Size: 12.7 KB)
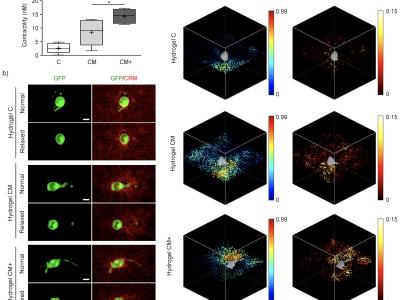
- Figure10_Traction force in 3D embedded cells.zip (Size: 1.25 GB)
- Supplementary Videos_Filopodia analysis in embedded cells_Supplementary Videos.zip (Size: 225.36 MB)
- Supplementary Figure1_Cell adhesion to ECM components.zip (Size: 8.79 KB)