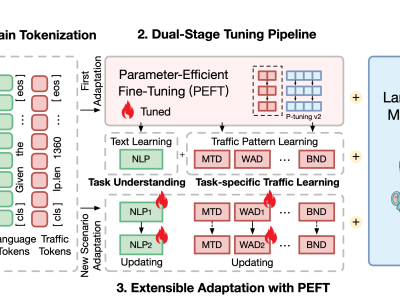
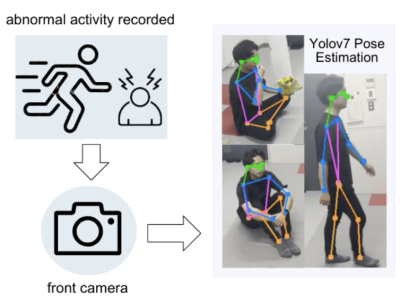
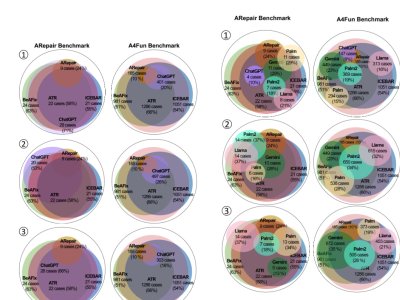
The LLM-RIMSA dataset, designed to advance 6G networks through ultra-massive connectivity and intelligent radio environments. The dataset is built around a novel framework that integrates large language models (LLMs) with a reconfigurable intelligent metasurface antenna (RIMSA) architecture. This integration addresses limitations in hardware efficiency, dynamic control, and scalability seen in existing RIS technologies.
- Categories: