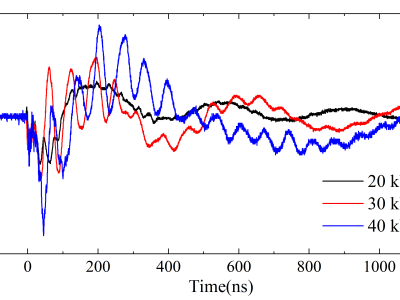
Coupled current waveforms at inverter #1 port PV+ for different field strengths.
- Categories:

Coupled current waveforms at inverter #1 port PV+ for different field strengths.

Offline-to-online is a key strategy for advancing reinforcement learning towards practical applications. This approach not only reduces the risks and costs associated with online exploration, but also accelerates the agent’s adaptation to real-world environments. It consists of two phases: offline-training and fine-tuning. However, offline-training and fine-tuning have different problems. In offline-training, the main difficulty is how to learn an excellent policy in a limited and incompletely distributed dataset.

Offline reinforcement learning aims to learn policies from a limited dataset without interacting with the environment. However, the restricted nature of the dataset limits the agent's understanding of the environment, leading to out-of-distribution (OOD) behavior and extrapolation errors. Conventional research can be categorized into four main approaches: Q-value penalties, policy constraints, uncertainty estimation, and importance sampling. Most existing methods impose overly strict penalties.

This data set is regarding the paper submitted to the IEEE Transactions on Molecular, Biological, and Multi-Scale Communications. The title of the paper is 'Molecular Signal Tracking and Detection Methods in Fluid Dynamic Channels' with the ID of TMBMC-TPS-19-0014.R2. The data are images taken from the particle image velocimetry (PIV) method and the Planar Laser-Induced fluorescence (PLIF) method. The images are being used to describe these two experimental methods for the molecular communication community.
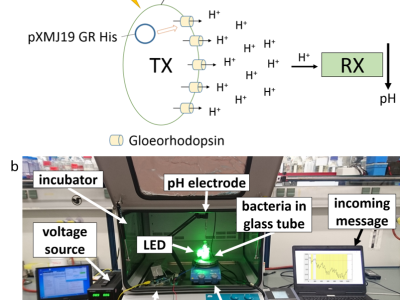
This data set is from a recent biological molecular communication (MC) testbed and provides a set of experimental measurement data.
In particular, the MC testbed is realized using Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria that express the light-driven proton pump gloeorhodopsin (GR) from Gloeobacter violaceus (G. violaceus).
Upon an external light stimulus, these bacteria (as the transmitter) export protons (as the signaling molecules) into the channel.
This changes the pH level of the environment, which can be detected with a pH sensor (as the receiver).