Datasets
Standard Dataset
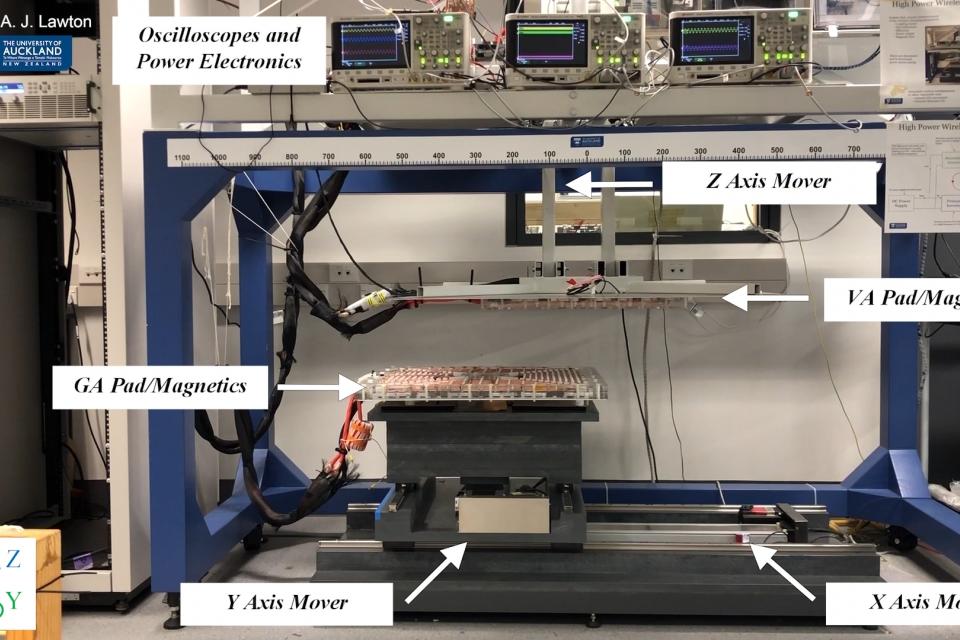
A Wireless Synchronization Controller for High-Power Stationary and Semi-Dynamic Wireless Charging of Electric Vehicles: Semi-Dynamic Wireless Synchronization Demonstration
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Patrick Lawton
- Last updated:
- Wed, 08/02/2023 - 04:02
- DOI:
- 10.21227/r4w1-fz84
- Data Format:
- License:
 227 Views
227 Views- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
This paper presents a vehicle side wireless synchronization controller suitable for high-power inductive power transfer (IPT) systems for electric vehicle (EV) wireless charging under stationary and semi-dynamic conditions. The objective of this work is to enable improved functionality, efficiency, and power density of high-power IPT systems under misaligned conditions. An existing 50 kW LCL-LCL tuned IPT system with dual active bridges (DAB) demonstrates the controller’s performance. The controller utilizes a decoupled auxiliary winding integrated into the vehicle assembly (VA) magnetics to wirelessly obtain the frequency and phase reference of the ground assembly (GA) active bridge to achieve synchronous switching and phase angle control of the VA active bridge. Experiments demonstrate this controller enables a 10.6% increase in power output and a 1.1% efficiency increase in regions of low coupling. Experiments also demonstrate the controller’s suitability for semi-dynamic applications, providing average power output and efficiency increases of 14.1% and 1.8% respectively, over 90% of the dynamic experiment range of magnetic alignments. Speed of synchronization, power output quality, and ease of implementation are discussed. Challenges associated with wireless synchronization in IPT systems are investigated, and recommendations are made regarding how they can be addressed.
A video demonstration of an experiment that showcases the proposed wireless synchronization controller operating under semi-dynamic conditions. This experiment was performed to validate research findings in the accompanying journal paper titled: "A Wireless Synchronization Controller for High-Power Stationary and Semi-Dynamic Wireless Charging of Electric Vehicles".