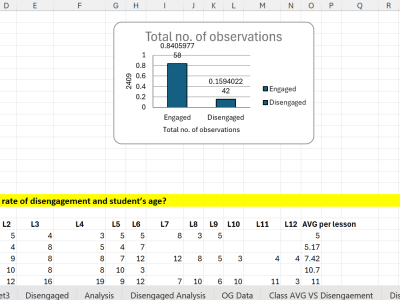
Studnets Disengagement Analysis
- Citation Author(s):
-
Shatha Radeef
- Submitted by:
- Shatha Radeef
- Last updated:
- DOI:
- 10.21227/ggn9-9a46
- Data Format:
 126 views
126 views
- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
Student disengagement is a critical challenge in educational environments, impacting learning outcomes and overall classroom dynamics. This study investigates the key factors contributing to student disengagement in classroom settings, focusing on environmental conditions, lesson types, student demographics, and specific disengagement behaviors. Conducted in a school in the United Arab Emirates, the research spans multiple lessons and subjects for students in Kindergarten and Elementary levels. The findings reveal that classroom temperature and lighting significantly influence disengagement, with higher temperatures and low light levels correlating with increased disengagement, particularly in subjects like Math and Science. Additionally, lesson types played a critical role, with interactive, hands-on activities showing lower disengagement compared to passive, lecture-based formats. The study also identified notable gender disparities in engagement, particularly in STEM subjects, where male students exhibited higher disengagement rates. Analysis of disengagement behaviors highlighted that idle behavior and excuses to leave the classroom were the most frequent forms of disengagement, posing challenges for detection and intervention. The study emphasizes the need for a multi-dimensional approach to address disengagement, involving optimized classroom environments, interactive teaching methods, and targeted strategies to meet individual student needs. These insights contribute to the development of more effective, evidence-based strategies to enhance student engagement and performance across diverse educational contexts.
Educational Impact and Implications Statement
This study provides actionable insights for educators and policymakers on addressing student disengagement in the classroom. It highlights the importance of optimizing environmental factors, such as classroom temperature and lighting, to reduce disengagement, especially in subjects like Math and Science. Interactive, hands-on activities are shown to be more effective in maintaining engagement than passive teaching methods. The findings also emphasize the need for targeted interventions to address gender disparities, particularly in STEM subjects, and to detect disengagement behaviors early. These insights support evidence-based strategies for creating more engaging and inclusive learning environments.
Instructions:
This dataset contains summarized data analysis related to the study. The key insights and processed data are available in the "Analysis_Per_L" sheet. This sheet provides structured analytical results that can be used for further evaluation. Additional raw data and calculations are available in other sheets for reference.