Datasets
Standard Dataset
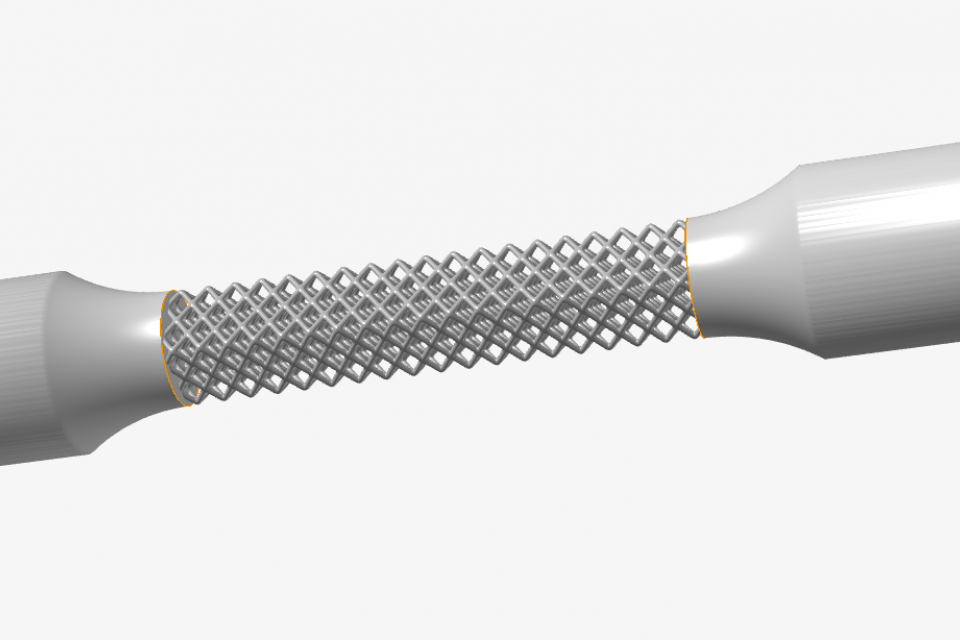
Graph Architected Lattice Materials based Tensile Samples
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- AKSHANSH MISHRA
- Last updated:
- Sat, 01/18/2025 - 18:10
- DOI:
- 10.21227/8865-vn62
- License:
 174 Views
174 Views- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
Architected materials, which are designed and engineered with specific microstructures, hold great promise for healthcare applications. In particular, tensile samples based on architected materials exhibit unique properties that can address key challenges in medical devices and implants. By precisely controlling the architecture at the micro- and nano-scale, these materials can be optimized for high strength-to-weight ratio, tunable stiffness, and enhanced biocompatibility.
Potential healthcare benefits of architected tensile samples include:
- Development of lightweight, high-strength materials for orthopedic implants that reduce stress shielding and promote bone ingrowth
- Creation of flexible yet resilient materials for soft tissue repair and tissue engineering scaffolds
- Engineering of smart materials with stimuli-responsive properties for drug delivery and biosensing applications
Through careful design of the material architecture, tensile properties can be tailored to match the mechanical behavior of native tissues. This architectural control also enables the incorporation of functional gradients and interconnected porosity to direct cellular responses.
- For the BCC unit cell, use a sample number of 1.
- For the SCC unit cell, use a sample number of 2.
- For the SC-BCC unit cell, use a sample number of 3.
- For the FCC unit cell, use a sample number of 4.
- For the Octet Truss unit cell, use a sample number of 5.
- For the Tesseract Truss unit cell, use a sample number of 6.
- For the Kelvin Truss unit cell, use a sample number of 7.
- For the Diamond unit cell, use a sample number of 8.