Power and Energy

This dataset includes figures related with the paper Dynamic Aggregation of Energy Storage Systems into Virtual Power Plants Using Distributed Real-time Clustering Algorithm.
- Categories:
 705 Views
705 Views
Data and results for the 36- and the 334-node test systems used for the integrated expansion planning problem of transmission and distribution systems.
- Categories:
 613 Views
613 Views
Text Book from Univ of Buenos Aires - Facultad de Ingeniería
- Categories:
 200 Views
200 Views
PowerGenerationofWT
- Categories:
 203 Views
203 Views
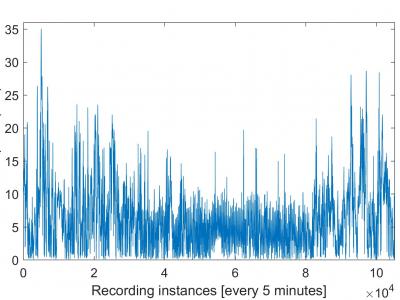
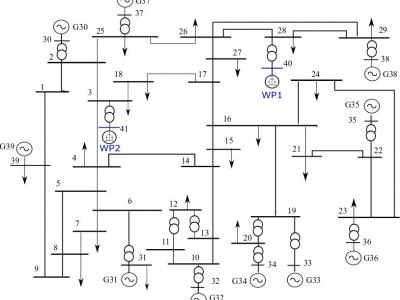
The uploaded data file is a part of data used or generated by a real time security system for frequency control in electrical grids with variable renewable generation proposed in a paper entitled: “Dynamic regulation in electrical networks with non-controlled sources”. The proposed security system analyzes the electrical network in both steady-state and dynamic state. The test systems IEEE 39-bus were used adding wind generation models to evaluate the proposed security system.
- Categories:
 684 Views
684 Views
The solenoid coil is designed to provide an inductance range of 200 to 300 microns to adjust the impedance. To simulate and calculate the inductance of the coil, two analytical methods and the finite element method have been used, which are the most common methods for calculating the inductance.
- Categories:
 138 Views
138 Views
The aim of this paper is to implement a modified Perturb and Observe algorithm (P&O), in order to solve the oscillations problem of photovoltaic (PV) power output generated by the conventional P&O algorithm. A comparison between the novel and the basic P&O algorithms is made. The first is implemented using embedded C language; the second is implemented using analog blocks. Next, the simulation study is made to present the response of the modified method to rapid temperature, solar irradiance and load change.
- Categories:
 197 Views
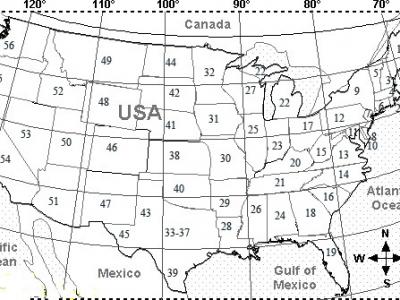
197 ViewsThe integrated power grid in USA is the largest in the world with the highest hourly power demand. In 2019, the highest hourly demand was more than 704 GW and the lowest hourly demand was less than 340 GW. The average daily variation in hourly demand is about 40% with respect to the highest hourly demand. A mathematical model is used to reduce the differential between peak and off-peak electrical power demand in this territory. The reduction is achieved with 5 time zones set up across US 48 states such that time difference between Far East and Far west is 4 hours.
- Categories:
 204 Views
204 Views