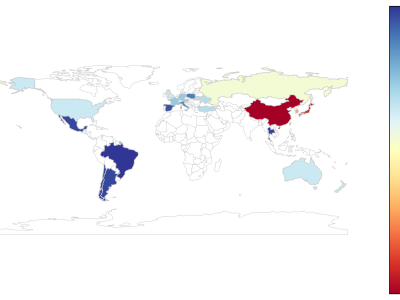
This dataset contains the data used in manuscript: "A Cross-language Analysis of User Reviews on Steam"
- Categories:

This dataset contains the data used in manuscript: "A Cross-language Analysis of User Reviews on Steam"

Four functional categories: communication, social networking, games, and audiovisual media.

Black Swan failures in aviation cybersecurity represent significant and unpredictable disruptions that stem from intricate interactions among behavioral drift, flaws in system design, and organizational inertia, thereby eluding conventional, pattern-based threat detection methodologies. This study presents the Black Swan Cyber Resilience Framework (BSCRF), which integrates principles of antifragility and supraresilience into the realm of cybersecurity, emphasizing adaptive learning over static defensive measures.

Short-range association fibers located in the superficial white matter play an important role in mediating higher-order cognitive function in humans. Detailed morphological characterization of short-range association fibers at the microscopic level promises to yield important insights into the axonal features driving cortico-cortical connectivity in the human brain yet has been difficult to achieve to date due to the challenges of imaging at nanometer-scale resolution over large tissue volumes.
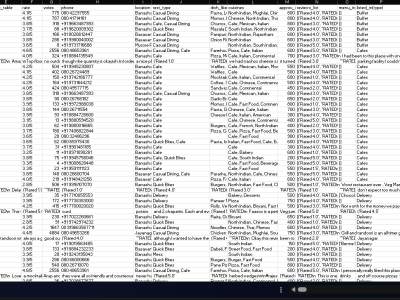
This dataset provides detailed information and customer reviews for restaurants listed on Zomato in Bangalore, with a focus on The Nest - The Den Bengaluru, located on ITPL Main Road, Whitefield. It includes key attributes such as location, contact details, rating, cuisines offered, average cost, and detailed user-generated reviews. The dataset is ideal for sentiment analysis, customer feedback mining, restaurant recommendation systems, and hospitality service quality studies.

This dataset provides detailed information and customer reviews for restaurants listed on Zomato in Bangalore, with a focus on The Nest - The Den Bengaluru, located on ITPL Main Road, Whitefield. It includes key attributes such as location, contact details, rating, cuisines offered, average cost, and detailed user-generated reviews. The dataset is ideal for sentiment analysis, customer feedback mining, restaurant recommendation systems, and hospitality service quality studies.

This dataset provides detailed information and customer reviews for restaurants listed on Zomato in Bangalore, with a focus on The Nest - The Den Bengaluru, located on ITPL Main Road, Whitefield. It includes key attributes such as location, contact details, rating, cuisines offered, average cost, and detailed user-generated reviews. The dataset is ideal for sentiment analysis, customer feedback mining, restaurant recommendation systems, and hospitality service quality studies.

This dataset proposes a new energy vehicle procurement decision-making framework that integrates data mining and social network group decision-making in an intuitive fuzzy environment. We use web crawler technology and social media public opinion analysis to capture and analyze text information about the performance of NEVs. 87,673 online blog posts about NEVs from December 1 to 31, 2024, were crawled from the API provided by the Sina Weibo Open Platform (https://weibo.com).

The Influence of the Pusdiklatkar Website Implementation on the Performance of Firefighters in DKI Jakarta This study aims to analyze the impact of implementing the Pusat Pendidikan dan Pelatihan Kebakaran (Pusdiklatkar) website on the performance of firefighters in DKI Jakarta. In the digital era, the utilization of information technology in training and personnel development has become increasingly crucial to enhancing work effectiveness and efficiency.