Datasets
Standard Dataset
A Dataset for Multi-Server Multi-User Computation Offloading
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Ruihuai Liang
- Last updated:
- Sat, 12/07/2024 - 21:47
- DOI:
- 10.21227/386p-7h83
- Data Format:
- License:
 611 Views
611 Views- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
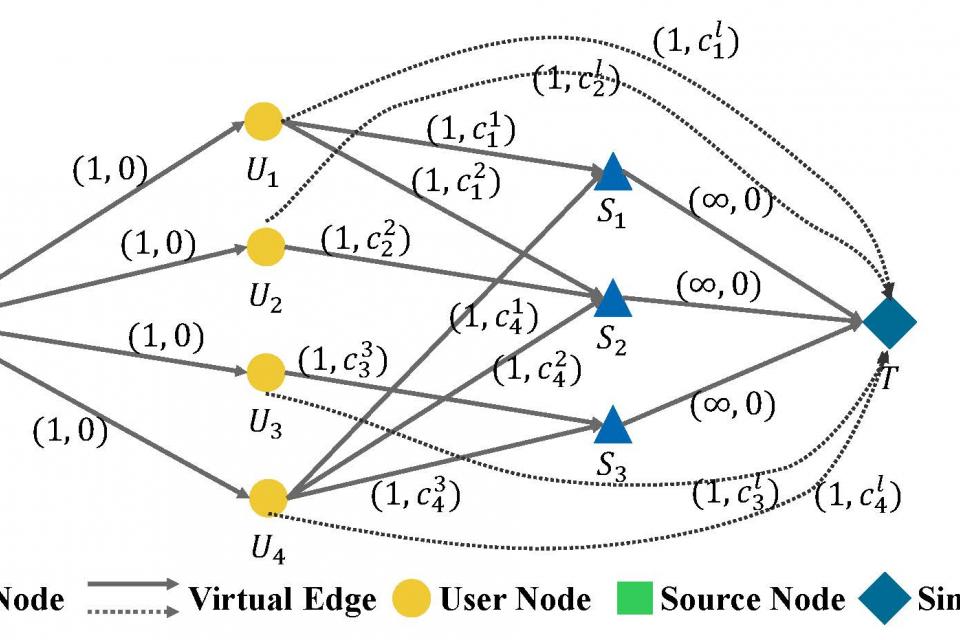
The Multi-Server Multi-User computation offloading (MSCO) dataset is a dataset based on the scenario of multi-server multi-user binary computing offloading. It is characterized by the connection status between users and edge servers, user task information, and server computational resource information. The solution aims to minimize the total cost of power consumption and latency of all tasks. The labels are the offloading decisions of user tasks and the computational resource allocation of edge servers. The features and labels of this dataset are graph-structured. The instance graphs in this dataset range in size from 9 to 88 nodes, offering tens of thousands of examples.
In the instruction pdf, we give the dataset format, as well as the relevant feature numerical ranges and statistical analysis of the dataset files. For each scale setting, there are two files with the same name in the dataset. The yaml file is the global parameter setting, and the txt file is the data body. Due to the large scale of the problem and the high complexity of the solution, all data files without the prefix "refine_" are suboptimal datasets. The difference in global cost after optimization with the optimal result is mostly less than 10%. The data files with the prefix "refine_" are small-scale truth value datasets of the corresponding scale data files. Each line in txt is a sample. The attribute names introduced in the dataset format are prefixed with "gt_" for labels, and the others are features. Therefore, when using it, just read the features as a directed graph with node features and edge features. The labels and features correspond to the same graph, but only some edges are retained in the labels as the result of offloading decisions and computational resource allocation. If necessary, you can also use the scripts we provide to read and preprocess the data.
Dataset Files
- Dataset body MSMU-CO.zip (2.72 GB)
- MSMU graph dataset process tool msco_graph_dataset.py (8.91 kB)
Documentation
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| 93.22 KB |






Comments
.
best