SSH & Telnet logs of HoneyCloud

- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Fan Dang
- Last updated:
- DOI:
- 10.21227/r7h4-gm51
- Research Article Link:
 120 views
120 views
- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
With the wide adoption, Linux-based IoT devices have emerged as one primary target of today’s cyber attacks. While traditional malware-based attacks (e.g., Mirai) can quickly spread across these devices, they are well-understood threats with defense techniques such as malware fingerprinting coupled with community-based fingerprint sharing. Recently, fileless attacks—attacks that do not rely on malware files—have been increasingly occurring on Linux-based IoT devices. Such attacks pose significant threats to the security and privacy of IoT systems; however, little has been known in terms of their characteristics and attack vectors, which hinders research and development efforts to defend against them.
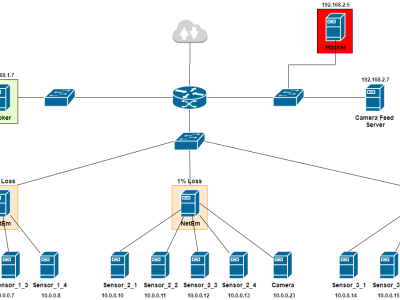
In this study, we present our endeavor in understanding fileless attacks on Linux-based IoT devices in the wild. Over a span of 12 months, we deployed four hardware IoT honeypots and 108 specially designed software IoT honeypots, which successfully attracted a wide variety of real-world IoT attacks. We present our measurement study on these attacks, with a focus on fileless attacks, including the prevalence, exploits, environments, and impacts. Our study further leads to multi-fold insights towards actionable defense strategies which can be adopted by IoT vendors and end users.
Instructions:
Code
We provide the customization code of HoneyCloud on GitHub.
Raw Data
We provide the login attemps data on GitHub.