Datasets
Standard Dataset
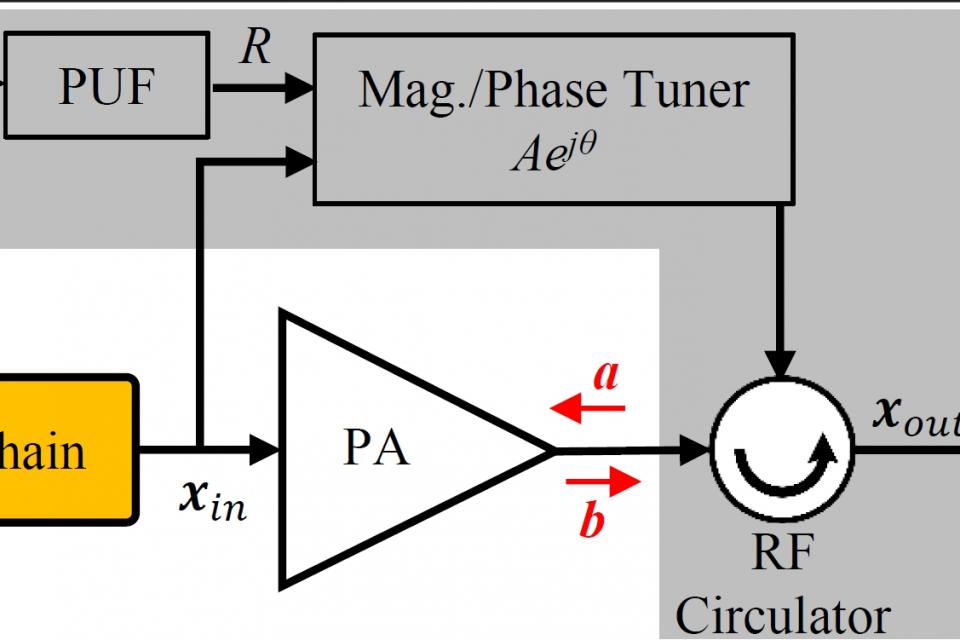
Radio Frequency Fingerprinting Exploiting Power Amplifier Active Load-pulling
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- YUEPEI LI
- Last updated:
- Thu, 05/16/2024 - 08:03
- DOI:
- 10.21227/vh95-rs64
- Data Format:
- License:
 460 Views
460 Views- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
A real world radio frequency fingerprinting (RFF) dataset for enhancement strategy by exploiting the physical unclonable function (PUF) to tune the RF hardware impairments in a unique and secure manner, which is exemplified by taking power amplifiers (PAs) in RF chains as an example. This is achieved by intentionally and slightly tuning the PA non-linearity characteristics using the active load-pulling technique. The dataset is collected from the cable-connected measurement and over-the-air measurement. The dataset includeds I/Q samples of received frames from 8 transmitters with same models of PA. The transmitter transmitted signal via USRP X310, and the USRP B210 as the receiver. The significance of this dataset is to enlarge the RFF feature differences among wireless devices of same vendor, in order to massively improve their RFF classification accuracy in low to medium signal to noise ratio (SNR) channel conditions. This approach is proposed to amplify the distinctions across same model PAs, thereby enhancing the RFF classification performance.
- The signal center frequency is 2.4 GHz.
- The dataset contains two experiments: cable-connected and over-the-air (OTA).
- We collect around 10s of duration for each emitter, and the sampling rate was set to 2 MHz.
- The I/Q samples are in 16-QAM modulation.
In the MATLAB code, the command load can be used to load the contents of the file.
More information, please refer to the README document.
Dataset Files
- pa1-cableconnected experiment.zip (59.98 GB)
- pa2-cableconnected experiment.zip (89.01 GB)
- pa3-cableconnected experiment.zip (121.35 GB)
- pa4-cableconnected experiment.zip (117.97 GB)
- pa5-cableconnected experiment.zip (124.59 GB)
- pa6-cableconnected experiment.zip (129.61 GB)
- pa7-cableconnected experiment.zip (126.17 GB)
- pa8-cableconnected experiment.zip (121.36 GB)
- 50 ohm test sample-cable connected experiment.zip (95.09 GB)
- 50 ohm OTA measurement.zip (61.59 GB)
- OTA measurement.zip (399.49 GB)
- PA loadpull measurement results PA loadpull measurement across 8 PAs.zip (68.73 MB)
Documentation