Datasets
Standard Dataset
Pediatric Walking
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Ales Prochazka
- Last updated:
- Mon, 11/04/2024 - 14:36
- DOI:
- 10.21227/f0hc-bw59
- Data Format:
- License:
 61 Views
61 Views- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
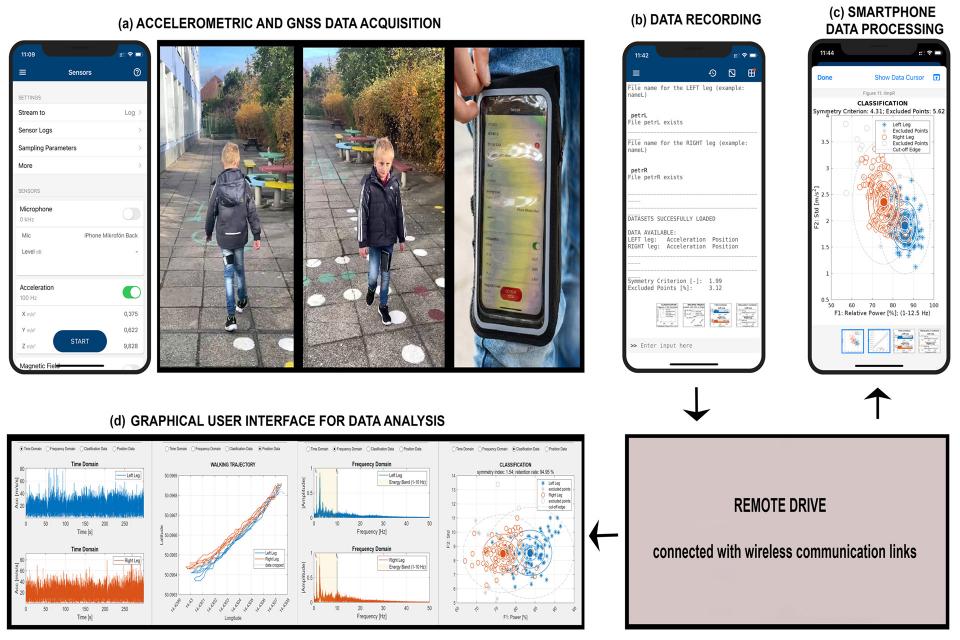
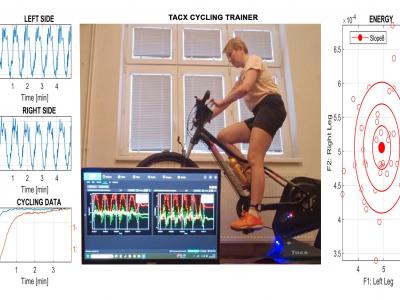
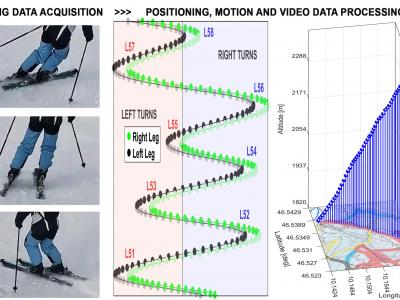
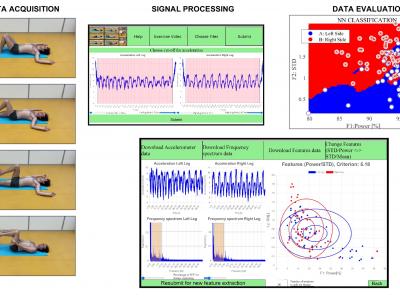
The study of motion data acquisition by wearable sensors and subsequent processing is a crucial research area with significant implications in monitoring physiological motion, identifying gait disorders, and classifying motion patterns, which is particularly relevant in pediatrics, neurology, and rehabilitation. This paper presents the utilization of accelerometric data to evaluate body motion symmetry in children, taking into account various factors such as age, diagnosis, and gender. The research employs mobile sensors to record signals under natural conditions, offering an innovative alternative to traditional clinical environment data acquisition. The whole dataset comprises signals gathered from 35 children, aged 10.8 +- 2.8 years, with their motion trajectories monitored via the global navigation satellite system. Our computational approach focuses on the analysis of accelerometric data, incorporating standard digital signal processing techniques, feature extraction in both time and frequency domains, and subsequent classification. The proposed methodology includes data acquisition by smartphone sensors, their wireless export to a remote drive, and data processing both by the proposed algorithm on the smartphone and by the graphical user interface. The classification methods include support vector machine, Bayesian analysis, k-nearest neighbor methods, and neural networks. This study aims to compare the symmetry level assessments made by specialists with an analysis of the correlation between body mass index and walking symmetry. Notably, a two-layer neural network achieved the highest classification accuracy of 92.0% in differentiating between two classes based on left and right body walking features, thus facilitating an analysis of varying symmetry levels. The results underscore the efficacy of general signal processing tools in applications such as rehabilitation, fitness movement monitoring, and neurological studies.
1. DatabaseWalk7 directory includes walking data of 35 children with accelerometers on the left and right legs
2. DatabaseWalk7.xlsx file describes all experiments
3. GUI_GaitAnalysis.mlapp file represents a graphical user interface for data processing
4. Mobile_GaitAnalysis.m file can be stored on MatlabDrive to acquire and process data by the mobile Matlab