Datasets
Standard Dataset
Gate voltage tunable temperature coefficient of resistance of WSe2 for thermal sensing applications
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Shubham Saxena
- Last updated:
- Mon, 12/05/2022 - 13:39
- DOI:
- 10.21227/mvem-c267
- Data Format:
- Links:
- License:
Abstract
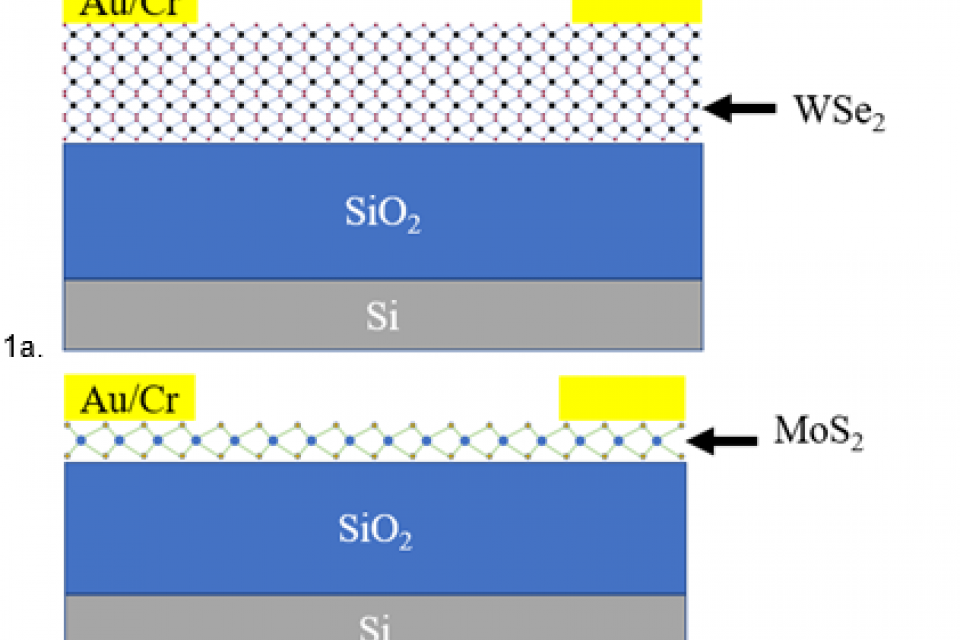
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have layered structure with unique properties. One of the properties of interest is the temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) which should be large for fast thermal sensors. The TCR is the calculation of the relative change in resistance per degree of temperature change. Taking a step further, tunable TCR is a concept that involves the control of TCR by the gate voltage. Here we have shown that in a field effect transistor device, the 2D semiconductor material WSe2 has a TCR, which can be controlled by varying the applied gate voltage. We also compared it with MoS2 and found that the WSe2 TCR is approximately six times that of MoS2 and 19 times that of metallic thin films. Also, WSe2 TCR could be controlled to 300% of its value within 10V of applied gate voltage. Specific high values of TCR can be tuned using the gate voltage as WSe2 TCR can be selected to -8.7 %K-1. This has applications in bolometers, thermal sensors, and accelerometers.
Details of the graphic files are provided in the attached documentation.
Documentation
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| 1.37 MB |
 163 Views
163 Views





Comments
ok for submit. thanks