continuous time Markov chains
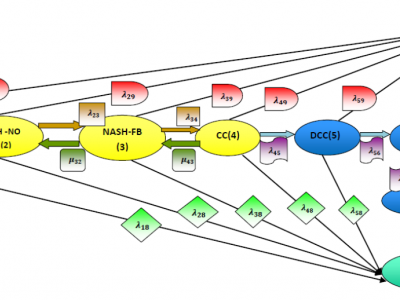
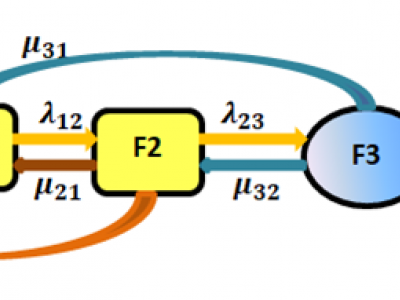
A global increase in the prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes is strongly connected to an increased prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) worldwide. In this article, the progression of the NAFLD process is modeled by continuous time Markov chains (CTMCs) with nine states. Maximum likelihood is used to estimate the transition intensities among the states. Once the transition intensities are obtained, the mean sojourn time and its variance are estimated, and the state probability distribution and its asymptotic covariance matrix are also estimated.
- Categories:
 193 Views
193 ViewsI tackle the problem of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) from the statistical point of view. Using the multistate model, in the form of the continuous time Markov chains, helps the statistical analysis of the progression of the disease over time. The simplest model of the health-disease-death process is applied to the NAFLD. The model is composed of 8 pdfs and 5 rates that need to be estimated. Maximum likelihood and quasi-Newton methods are applied to estimate the transition rates among states.
- Categories:
 167 Views
167 Viewsone hundred fifty patients were followed up every year for 28 years, and at each visit the characteristics of the patients were recoreded ( these are the predictors) like: sex( 0= female, 1= male) , age, BMI, LDL-chol, HOMA2-IR, systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. For each partipant, the recorded value is the mean of the follow up measurements. The age is the median value. The response variables are the transition counts among the states of the process of the disease ( fibrosis in NAFLD ) evolving over time .
- Categories:
 208 Views
208 Views