Wind speed data

- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Huong Le
- Last updated:
- DOI:
- 10.21227/bfbf-qr46
- Data Format:
 4 views
4 views
- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
The integration of electrolyser systems into offshore wind farms (OWF) via high-voltage direct current (HVDC) networks offers a promising solution that could increase the value and reduce the costs associated with large-scale hydrogen production, enabling green hydrogen production and the provision of energy storage and grid ancillary services. This paper presents the modeling and integrating of large-scale electrolyser plants within HVDC-connected OWF to evaluate the benefits of these systems. Mathematical modelling of these integrated systems is performed, incorporating average models, and control algorithms. A simplified model is developed to simulate operational scenarios, accounting for wind variations, HVDC grid constraints, and electrolyser response characteristics, and the system is applied to several case studies including demand response and frequency response scenarios. The results demonstrate the potential benefits of using excess wind energy for hydrogen production in these systems which include reducing curtailment and enhancing the overall exported energy yield of the OWF. This work provides a foundational framework for the deployment of hydrogen production facilities in offshore wind environments, contributing to the advancement of sustainable energy systems.
Instructions:
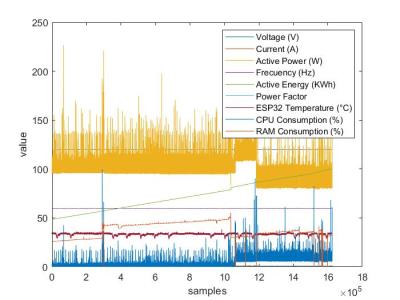
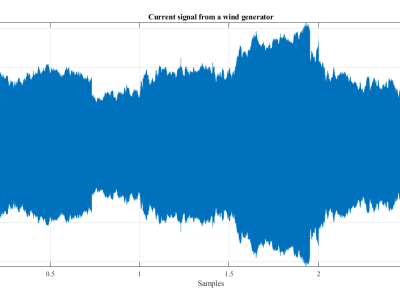
Time-series wind data: column 1 is time, column 2 is wind speed