Datasets
Standard Dataset
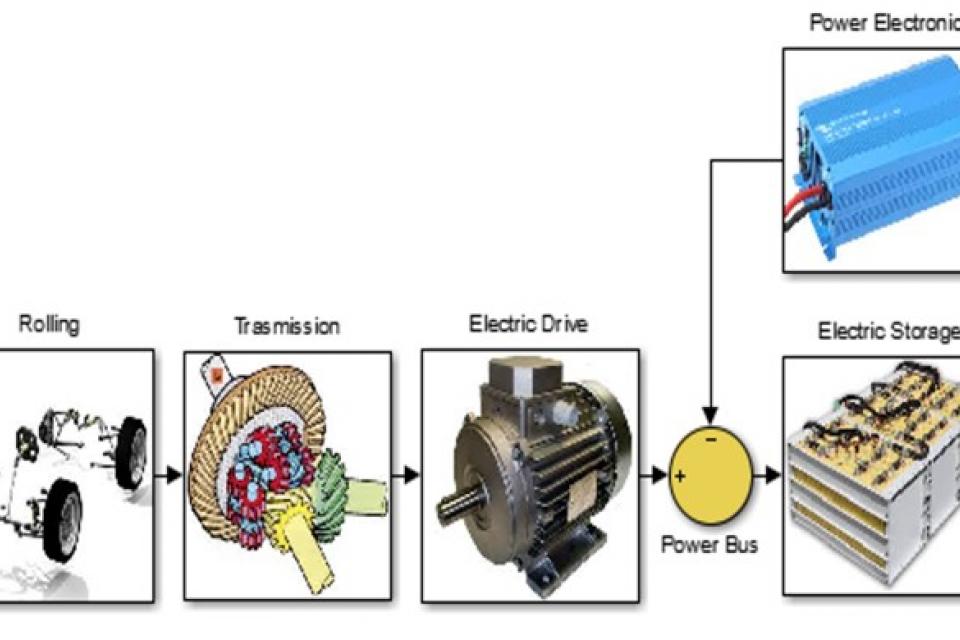
On specific energy consumption of conventional, series hybrid and fully electric buses
- Citation Author(s):
- Carlo Villante
- Submitted by:
- Carlo Villante
- Last updated:
- Fri, 11/22/2024 - 10:23
- DOI:
- 10.21227/H2M62R
- License:
 461 Views
461 Views- Categories:
Abstract
Making use of a specifically designed SW tool, the authors here presents the results of an activity for the evaluation of energy consumption of buses for urban applications. Both conventional and innovative transport means are considered to obtain interesting comparative conclusions. The SW tool simulates the dynamical behaviour of the vehicles on really measured paths making it possible to evaluate their energetic performances on a Tank to Wheel (TTW) basis. Those data, on such a wide and comparable range were still unavailable in literature.
Results are also extended to a Well to Wheel (WTW) basis making use of numerical and experimental results about Well to Tank (WTT) energy consumption by the Joint Research Centre of the European Union, to take into account potential benefits for the community connected with different energy vectors use. Sensitiveness of energy consumption with the main influencing parameters was evaluated in coherence with the CorinAIR approach defined within the UE and already applied only to conventional means. By this approach, the presented results, as well as the SW tool will soon be part of an integrated Decision Support System (DSS) to be used by local transportation authorities
Data refer to WTW enery fluxes in conventional, series hybrid and fully electric buses