RSSI_Indoor_IICUT

- Citation Author(s):
-
Ruvan Abeysekara (IIC University of Technology)
- Submitted by:
- M.W.P Maduranga
- Last updated:
- DOI:
- 10.21227/pdb2-g864
- Data Format:
 265 views
265 views
- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
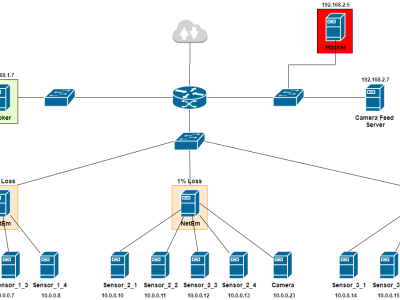
The Internet of Things (IoT) technology has revolutionized every aspect of everyday life by making everything smarter. IoT became more popular in recent years due to its vast applications in many fields such as smart cities, agriculture, healthcare, ambient assisted living, animal tracking, etc. Localization of a sensor node refers to knowing a sensor node's geographical location in the IoT network. In this research, we propose a device free indoor localization mechanism based on the Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI), a measure of the receiving signal from the sensor nodes, and supervised Machine Learning (ML) algorithms. An experimental test-bed was implanted in a controlled environment to collect RSSI values from the sensor nodes. The RSSI levels were collected by using multiple and published to a remote MQTT server over the Internet. In this research, RSSI values were used to train supervised ML algorithms, Linear Regression (LR), Polynomial Regression (PR), Decision Tree Regression (DTR), Support Vector Regression (SVR), and Random Forest Regressor (RFR) to estimate the accurate positioning of IoT related localization applications. The error between the actual measured values of the position and the estimated values are compared to validate the system model presented
Instructions:
The Internet of Things (IoT) technology has revolutionized every aspect of everyday life by making everything smarter. IoT became more popular in recent years due to its vast applications in many fields such as smart cities, agriculture, healthcare, ambient assisted living, animal tracking, etc. Localization of a sensor node refers to knowing a sensor node's geographical location in the IoT network. In this research, we propose a device free indoor localization mechanism based on the Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI), a measure of the receiving signal from the sensor nodes, and supervised Machine Learning (ML) algorithms. An experimental test-bed was implanted in a controlled environment to collect RSSI values from the sensor nodes. The RSSI levels were collected by using multiple and published to a remote MQTT server over the Internet. In this research, RSSI values were used to train supervised ML algorithms, Linear Regression (LR), Polynomial Regression (PR), Decision Tree Regression (DTR), Support Vector Regression (SVR), and Random Forest Regressor (RFR) to estimate the accurate positioning of IoT related localization applications. The error between the actual measured values of the position and the estimated values are compared to validate the system model presented