A Multisensor Fusion Method Based on High-Dimensional Cognitive Encoding for Large-Scale Navigation
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Chenxu Wang
- Last updated:
- DOI:
- 10.21227/nstk-y264
 8 views
8 views
- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
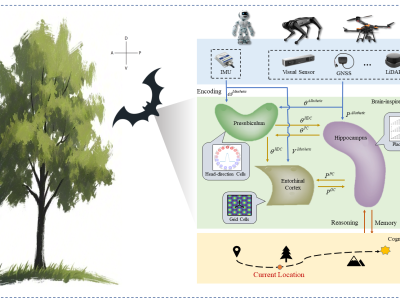
With the widespread application of unmanned systems in large-scale and complex environments, accurate and reliable navigation has become a pivotal challenge. Most existing brain-inspired multisensor fusion methods primarily focus on small-scale environments and overlook the impact of high-dimensional cognitive information on navigation. In this article, inspired by the navigation mechanisms of the bat brain, we propose a multisensor fusion navigation architecture based on memory and reasoning mechanisms. The proposed architecture adaptively integrates multisensor information in high-dimensional cognitive space through environmental perception, spatial perception, and cognitive reasoning. To further improve navigation performance, we propose a place cell update method based on cyclic mapping and a cognitive map decoding method based on interest iteration. The proposed method is evaluated on both public datasets and our own dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed brain-inspired multisensor fusion method outperforms existing methods in terms of localization accuracy and robustness, offering a promising brain-inspired solution for large-scale navigation tasks.
Instructions:
Please enter or select via autocomplete one or more terms that will help others find your data competition.