Datasets
Standard Dataset
Matrix-scaled consensus on socfb-Amherst41 dataset
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Minh Trinh
- Last updated:
- Mon, 04/15/2024 - 01:17
- DOI:
- 10.21227/n39p-qa92
- Data Format:
- Research Article Link:
- Links:
- License:
 376 Views
376 Views- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
Simulation of the matrix-scaled consensus algorithm [1,2] on the network derived from the dataset socfb-Amherst41 [3,4].
References
[1] Trinh, M. H., Vu, D. V., Tran, Q. V., and Ahn, H.-S. "Matrix-scaled consensus." In Proc. of the 61st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), pp. 346-351. IEEE, 2022. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.10723 (2022)
[2] Trinh, M. H., Vu, H. H., Le-Phan, N.-M., and Nguyen, Q. N. "Matrix-Scaled Consensus over Undirected Networks." arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.14751 (2023).
[3] Rossi, Ryan, and Nesreen Ahmed. "The network data repository with interactive graph analytics and visualization." In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol. 29, no. 1. 2015.
We perform the matrix-scaled consensus (MSC) algorithm [1,2] on the dataset socfb-Amherst41 [3]. The dataset is available for download at [4].
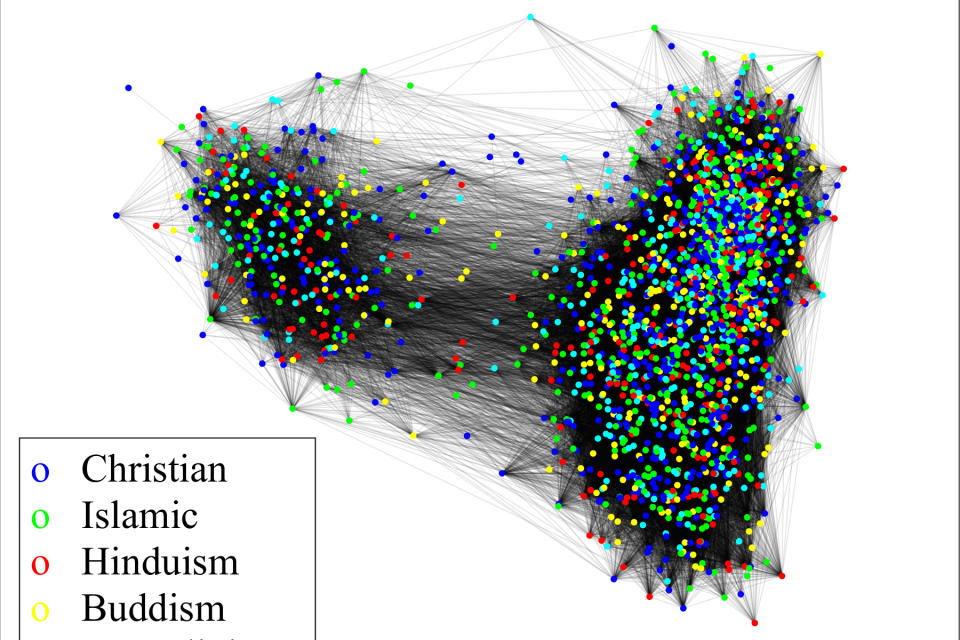
- The network attracted from the dataset is used as the interaction graph for the simulation. The graph is undirected, connected and contains 2235 vertices and 90954 edges.
- We assume that the people in the network are classified into five major groups based on their religion beliefs (No religion, Buddhism & Folk religion, Hinduism, Islam, Christianity). Since the dataset does not provide each individual's religion, we use randomization to assign each individual into 5 groups. The probability for an idividual to be classified with a given religion is derived from the data in []
- Each group is assigned a corresponding 2x2 SO(2) scaling matrix. The non-religion group is assigned with the 2x2 identity matrix. Three factors are considered for determining the scaling matrix of the other groups: God(s), Afterlife, and Attitude towards alcohol as described in the Table 1 (a '+' corresponding to a +pi/4 rotation CCW, and a '-' corresponds to a -pi/4 rotation CCW).The references for these factors can be found at [6].
- The simulation results include: the network with colors indicating religion groups; the initial opinion vectors [x_i; y_i] of the 2235 agents are randomly generated (x_i, y_i take values between 0 and 1), and snapshots of the simulations at severral time instant between 0 to 10 seconds.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Criteria \ Group | No religion | Buddism & Folklore religion | Hinduism | Islam | Christianity |
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
God(s) | No | Multiple Gods (+) | Multiple Gods (+) | One God (-) | One God (-) |
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Afterlife | No | Rebirth or nirvana (+) | Reincarnation until attaining liberation (+) | Paradise or Hell (-) | Heaven or Hell (-) |
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Alcohol | No prefference | Prohibited (-) | No prohibition (+) | Not allowed (-) | No prohibition (+) |
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Scaling matrix | eye(2) | Rot(+\pi/4) | Rot(+3\pi/4) | Rot(-3\pi/4) | Rot(-\pi/4) |
_________________________________________________________________________________________
Table 1: Comparison of 5 major religious groups based on three criteria. A "+" means more openess and a "-" means more conservative. Each '+' accounts for +pi/4 CCW rotation and each '-' accounts for a -pi/4 CCW rotation in the scaling matrix.
References
[1] Trinh, M. H., Vu, D. V., Tran, Q. V., and Ahn, H.-S. "Matrix-scaled consensus." In Proc. of the 61st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), pp. 346-351. IEEE, 2022. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.10723 (2022)
[2] Trinh, M. H., Vu, H. H., Le-Phan, N.-M., and Nguyen, Q. N. "Matrix-Scaled Consensus over Undirected Networks." arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.14751 (2023).
[3] Rossi, Ryan, and Nesreen Ahmed. "The network data repository with interactive graph analytics and visualization." In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol. 29, no. 1. 2015.
[4] https://networkrepository.com/socfb-Amherst41.php
[5] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Major_religious_groups
[6] https://religionfacts.com/big-religion-chart






Comments
Version 1, April 15, 2024