Datasets
Standard Dataset
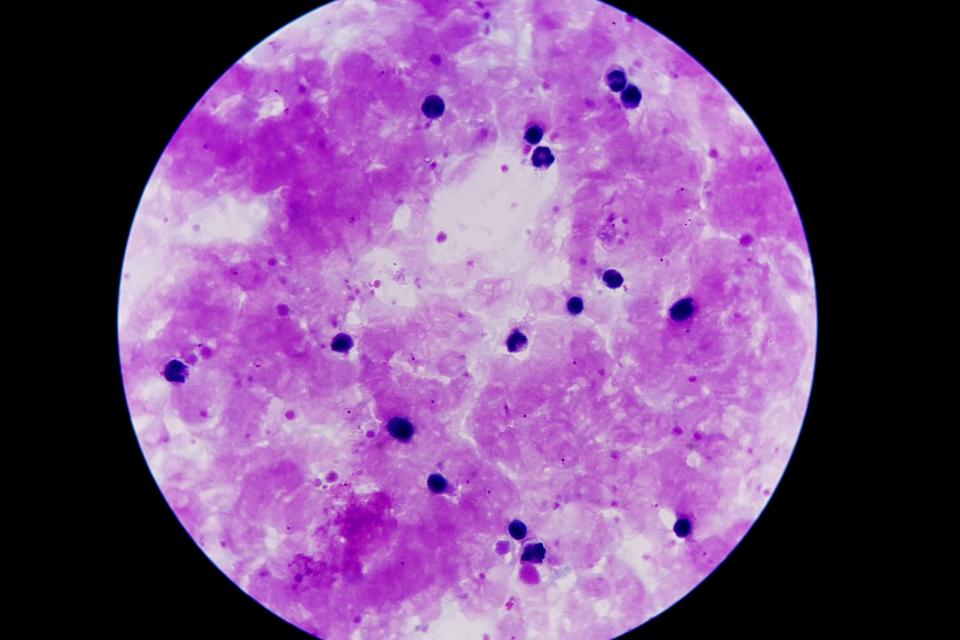
Malaria Thick Blood Smears
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Feng Yang
- Last updated:
- Tue, 08/03/2021 - 17:18
- DOI:
- 10.21227/qsqw-a673
- Data Format:
- Links:
- License:
 6946 Views
6946 Views- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
We photographed Giemsa-stained thick blood smear slides from 150 P. falciparum infected patients at Chittagong Medical College Hospital, Bangladesh, using a smartphone camera for the different microscopic field of views. Images are captured with 100x magnification in RGB color space with a 3024×4032 pixel resolution. An expert slide reader manually annotated each image at the Mahidol-Oxford Tropical Medicine Research Unit (MORU), Bangkok, Thailand. We de-identified all images andtheir annotations, and archived them at the National Library of Medicine (IRB#12972).
Reference:
We request that publications resulting from the use of this data attribute the source (National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) and cite the following publication, which has used the data for parasite detection and classification:
Feng Yang, Mahdieh Poostchi, Hang Yu, Zhou Zhou, Kamolrat Silamut, Jian Yu, Richard J Maude, Stefan Jaeger, Sameer Antani. Deep Learning for Smartphone-based Malaria Parasite Detection in Thick Blood Smears. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 24(50): 1427-1438, 2020. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2019.2939121.
The whole dataset can also be downloaded on: https://data.lhncbc.nlm.nih.gov/public/Malaria/Thick_Smears_150/index.html.
This dataset includes blood smear images from 150 malaria infected patients, with 12 images per patient on average.
Images are stored in: \Thick_Smears_150\[PatientName]\[ImageName].jpg
Corresponding annotations are stored in the following subfolder: \GT_updated\[PatientName]\[ImageName].txt.
The annotations include the positions of parasites and white blood cells, in image coordinates. In each annotation file, the first line contains three numbers: The first number is the total number of parasites and white blood cells in the image. The second number is the image height and the third number is the image width. All following lines are annotations of parasites and white blood cells.
If the second entry in a line is “Parasite,” this line represents an annotated parasite. Otherwise, if the second entry is “White_Blood_Cell”, this line is the annotation of a white blood cell. The fourth entry indicates whether a parasite or white blood cell has been annotated as a “Circle” or “Point”. In case of a circle, columns six and seven are the x- and y-coordinates of the circle center, and columns eight and nine are the coordinates of a random point on the circle. In case of a point, columns six and seven are the coordinates of this point.
Documentation
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| 933.95 KB |