Datasets
Standard Dataset
Data for Super-High-Frequency Low-Loss Sezawa Mode SAW Devices in a GaN/SiC Platform
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Imtiaz Ahmed
- Last updated:
- Fri, 11/18/2022 - 21:13
- DOI:
- 10.21227/nhsd-jw66
- License:
 137 Views
137 Views- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
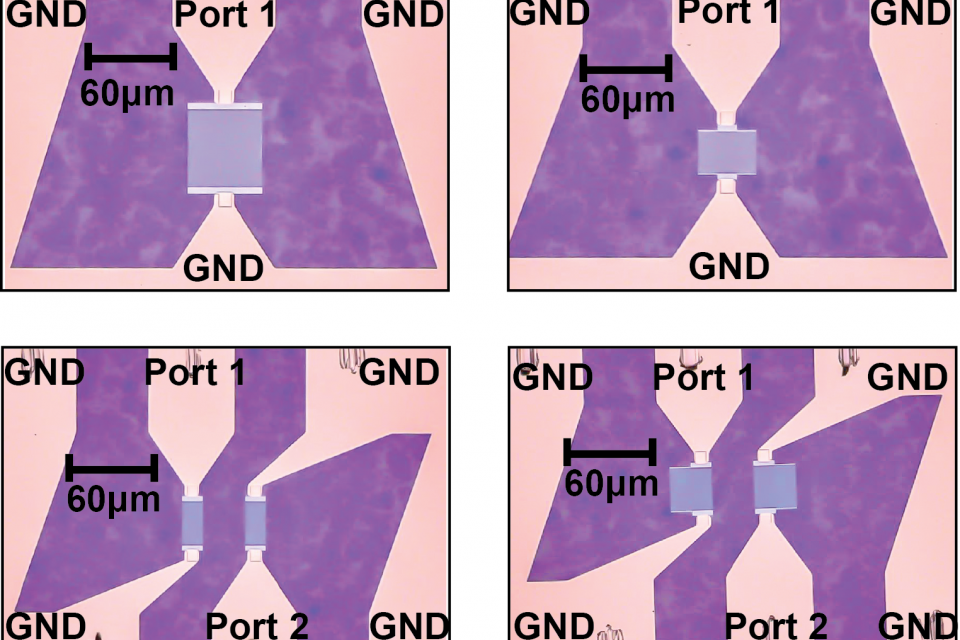
This work presents a comprehensive study of the performance of Sezawa surface acoustic wave (SAW) devices in SweGaN QuanFINE® ultrathin GaN/SiC platform, reaching frequencies above 14 GHz for the first time. Sezawa mode frequency scaling is achieved due to the elimination of the thick buffer layer typically present in epitaxial GaN technology. Finite element analysis (FEA) is first performed to find the range of frequencies over which the Sezawa mode is supported in the grown structure. Transmission lines and resonance cavities driven with Interdigital Transducers (IDTs) are designed, fabricated, and characterized. Modified Mason circuit models are developed for each class of devices to extract critical performance metrics. We observe a strong correlation between measured and simulated dispersion of the phase velocity and piezoelectric coupling coefficient. Maximum coupling of 0.61% and frequency-quality factor product of 6×1012 s-1 are achieved for Sezawa resonators at 11 GHz, with a minimum propagation loss of 0.26 dB/λ for the two-port devices. Sezawa modes are observed at frequencies spanning up to 14.3 GHz, achieving a record high in GaN microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) to the best of the authors’ knowledge.
All scattering parameters (S-parameters) files obtained from experimental measurements for different Sezawa mode devices discussed in the work are added to the zipped folders. The excel file contains all circuit parameters extracted by fitting measured data using the modified Mason model for IDTs, resonators, and delay lines. It also includes data obtained from FEA simulation in COMSOL.
Dataset Files
- 1Port IDTs.zip (1.58 MB)
- 1Port Resonators.zip (1.57 MB)
- 2Port Delay Lines.zip (2.97 MB)
- 2Port Resonators.zip (2.97 MB)
- All Extracted Parameters.xlsx (74.27 kB)