Br35H :: Brain Tumor Detection 2020
- Citation Author(s):
-
Ahmed Hamada
- Submitted by:
- Zheng Linxuan
- Last updated:
- DOI:
- 10.21227/tbkk-q937
 551 views
551 views
- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
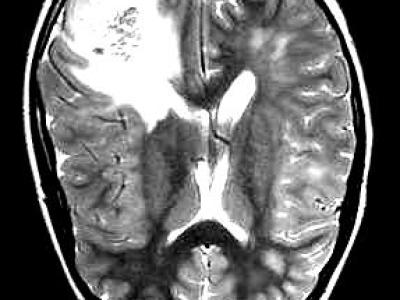
A Brain tumor is considered as one of the aggressive diseases, among children and adults. Brain tumors account for 85 to 90 percent of all primary Central Nervous System(CNS) tumors. Every year, around 11,700 people are diagnosed with a brain tumor. The 5-year survival rate for people with a cancerous brain or CNS tumor is approximately 34 percent for men and36 percent for women. Brain Tumors are classified as: Benign Tumor, Malignant Tumor, Pituitary Tumor, etc. Proper treatment, planning, and accurate diagnostics should be implemented to improve the life expectancy of the patients. The best technique to detect brain tumors is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). A huge amount of image data is generated through the scans. These images are examined by the radiologist. A manual examination can be error-prone due to the level of complexities involved in brain tumors and their properties.
Application of automated classification techniques using Machine Learning(ML) and Artificial Intelligence(AI)has consistently shown higher accuracy than manual classification. Hence, proposing a system performing detection and classification by using Deep Learning Algorithms using Convolution-Neural Network (CNN), Artificial Neural Network (ANN), and Transfer-Learning (TL) would be helpful to doctors all around the world.
Instructions:
Br35H public dataset, which includes 801 annotated brain tumor MRI images. The dataset is divided into a training set (500 images), a validation set (201 images), and a test set (100 images), used for model training, validation, and testing, respectively.



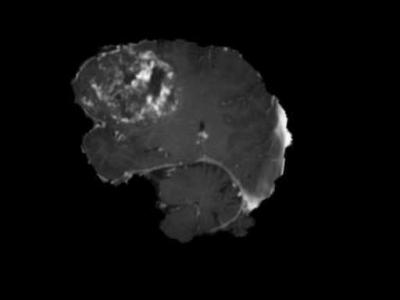






i want this dataset for Research pupose.