Datasets & Competitions
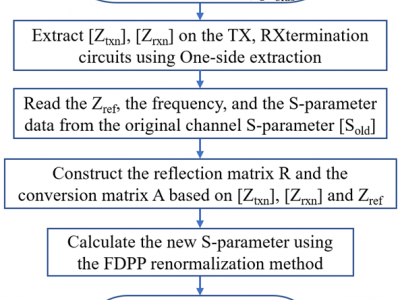
A Frequency-Dependent & Per-Port (FDPP) channel termination & renormalization method is presented as
a more accurate substitute for the traditional method which
uses frequency-independent, uniform impedance as the serialization/deserialization (SerDes) transmit (TX)/receive (RX)
termination impedances. Although the traditional method is
employed in practically all the existing high-speed interface
standards, the assumption of the constant, uniform termination
impedance at TX and RX is not exact and will lead to inaccuracy.
- Categories:
 34 Views
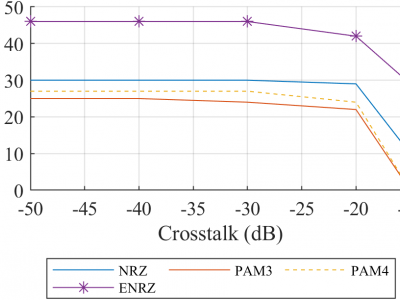
34 ViewsThe performances of ENRZ (Ensemble NRZ) under
the interferences of crosstalk, in conjunction with NRZ (NonReturn-to-Zero), PAM4 (Pulse Amplitude Modulation of 4-level),
and PAM3 are investigated. One-side and two-side crosstalk scenarios with varying levels of crosstalk are studied. The simulated
eye-diagram obtained with the four signaling techniques under
a range of crosstalk levels are compared and the reasons that
lead to the prominent advantages of ENRZ are analyzed. As
an alternative approach of validating the performances of the
- Categories:
 102 Views
102 Views