Datasets
Standard Dataset
Big Data from Two Area LFC System during Normal and Cyber-Attack Conditions
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Sneha B V
- Last updated:
- Fri, 05/03/2024 - 23:20
- DOI:
- 10.21227/sc80-2t97
- Data Format:
- License:
 505 Views
505 Views- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
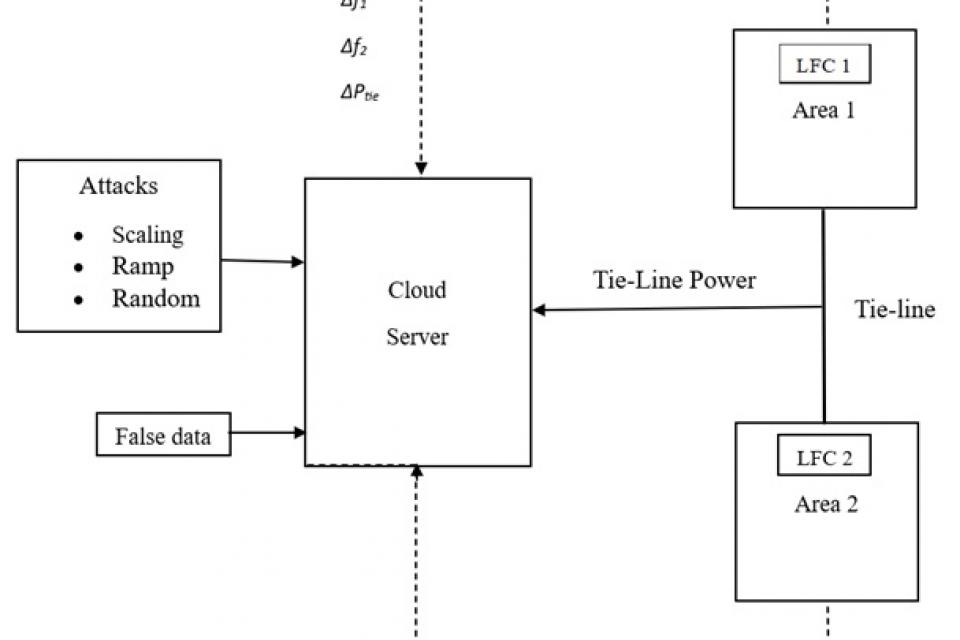
The efficient operation of interconnected power systems relies on Load Frequency Control (LFC) to maintain stable frequency and regulate tie-line power flow between distinct areas. In modern setups, LFC parameters are monitored and processed in real-time through cloud-based platforms, enabling centralized control and optimization. However, this introduces vulnerabilities, as demonstrated by the susceptibility to attacks such as scaling, ramp, and random manipulations of data transmitted between areas and the cloud server. These attacks compromise the integrity of LFC, leading to system instability and the risk of grid collapse. This underscores the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures to fortify LFC systems against malicious intrusions. By analyzing datasets of LFC operations under attack scenarios, AI techniques can be employed for attack identification and mitigation. Such efforts are pivotal in ensuring the resilience and reliability of power system operations in the face of evolving cyber threats. Through a multidisciplinary approach integrating power systems engineering and cybersecurity and this aims to enhance the security posture of LFC systems, thereby safeguarding critical infrastructure and mitigating potential disruptions to energy supply.
The datasheet provides information of frequency in area1, frequency in area 2 and the tie-line power for the load variations and scaling, ramp, random attacks.
Dataset Files
- Two area LFC with scaling, ramp and random attacks - 50k dataset LFC-Attack-50kdata.xlsx (2.25 MB)
- Two area LFC with scaling, ramp and random attacks - 18k dataset LFC-Attack-18kdata.xlsx (853.90 kB)
Documentation
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| 273.99 KB |