Dataset Entries from this Author
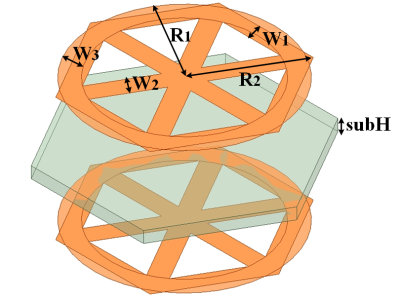
- Categories:
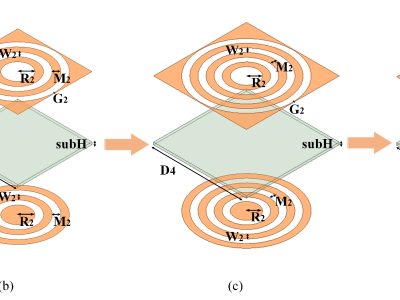
- Categories:
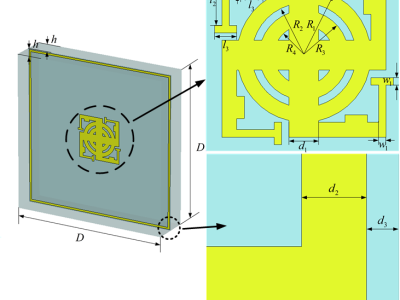
Abstract-In this paper a FSS-based absorber:with highabsorption effciency is proposed in the terahertz regime foruse in communications applications. It has the potential toenhance the performance of communication systems, minimizesignal interference, and guarantee the stability and effciencyof data transmission, The structure of this terahertz absorbercomprises annular patches and shaped patches.
- Categories:
In this letter, a miniaturized and dual-stopband frequency selective surface(FSS) with a large band ratio(BR) is presented. This structure is composed of one metal layer and two dielectric layers and has excellent miniaturization characteristics. In particular, the unit size is only 0.054λ0 and the thickness is only 0.014λ0, where λ0 is the wavelength corresponding to the first resonant frequency. And there is only one layer of metal layer, which greatly reduces the processing complexity and cost.
- Categories:

original model of structure
- Categories:

original model of structure
- Categories:
