Dataset Entries from this Author
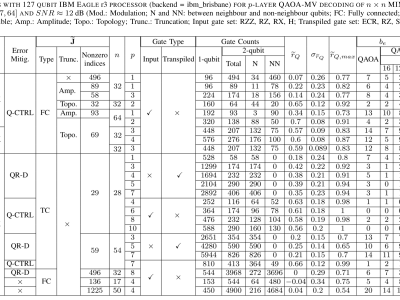
The data repository contains data sets obtained with Quantum-approximate optimization algorithm (QAOA) simulations and experiments for the main article in [1]. For a comprehensive understanding, please check readme_qaoa_mvsic.pdf file and refer to the main article in [1]. We design, theoretically model, simulate and experiment QAOA-MVSIC algorithm combining QAOA, majority voting (MV) and successive interference cancellation (SIC) to target experimental challenges of QAOA for maximum-likelihood (ML) decoding for n × n massive multi-input multi-output (MIMO) systems with large n.
- Categories:
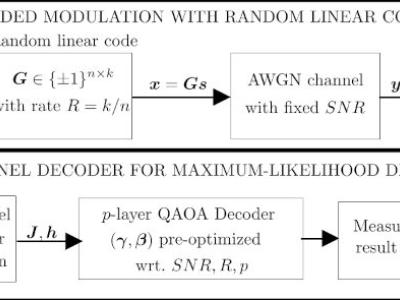
The data repository includes simulation parameters and results for the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) channel decoding applied to short block-lengths in Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) channels. This research utilizes a Random Linear Code (RLC) in a Coded Modulation (CM) design at the encoder. Extensive simulations were conducted using IBM Quantum Lab and the ibmq_qasm_simulator back-end provided by IBM Quantum, simulating quantum circuits on classical hardware.
- Categories:
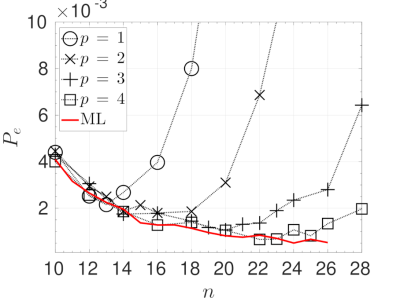
- Categories:
