Datasets
Standard Dataset
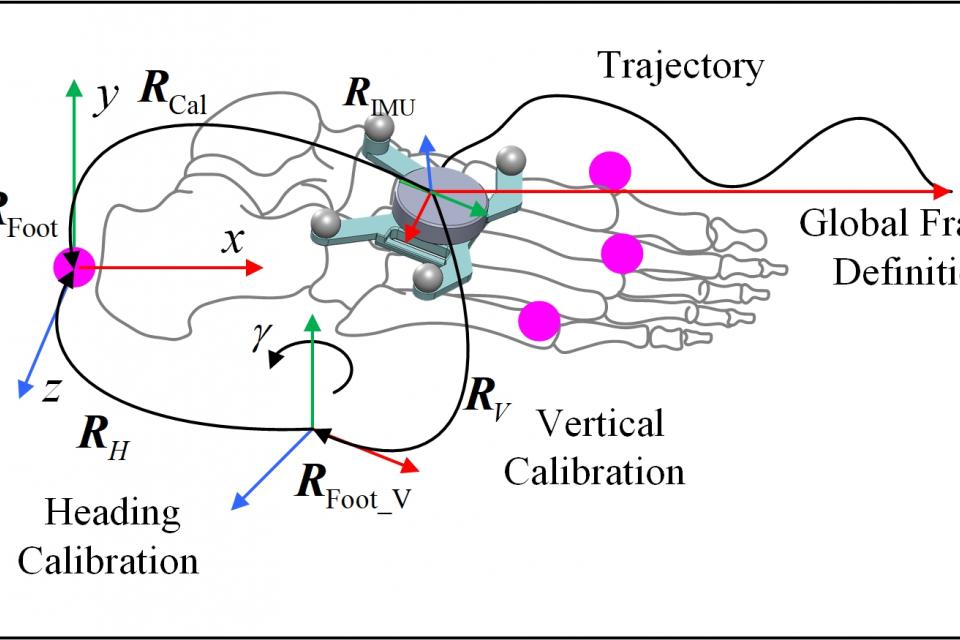
Plug-and-Play IMU-based Gait Measurement: Towards 3D Foot Angle Estimation
- Citation Author(s):
- Submitted by:
- Zhengtao Wang
- Last updated:
- Mon, 11/25/2024 - 04:04
- DOI:
- 10.21227/c7w9-a205
- License:
 84 Views
84 Views- Categories:
- Keywords:
Abstract
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a common joint disease, causing pain, stiffness and other motor disorders. Gait analysis is an important basis for understanding the causes and formulating personalized rehabilitation plans. Although optical motion capture is regarded as the gold standard for measurement, it has drawbacks such as high cost and being limited to laboratories. Inertial measurement units (IMUs) offer an out-of-lab gait measurement method, but the accuracy of the measurements relies heavily on the participants’ performance of the calibration movement, posing challenges for patients with gait abnormalities. Although in previous studies, this had little effect on the measurement of sagittal angle, it has a significant impact on the measurement internal and external rotation. The range of internal and external rotation of the ankle joint is very small. Excessive external rotation of foot may indicate excessive external rotation of the knee joint. Therefore, accurate measurement of 3D foot angles, especially internal and external rotation, is important for KOA. We proposed a gait measurement method, the calibration process will be non-sensory for the user. We recruited 20 healthy subjects 8 KOA patients. The root mean square errors of foot angles range from 3.0° to 6.6° in three directions. We investigated the influence of abnormal gait on calibration and determined that our calibration method is less affected by gait abnormalities. Therefore, this method is also expected to be applied to other patients with abnormal gait.
Run in sequence KOAPatient\KOA2_TimeAlign.mlx, KOAPatient\KOA3_OMCGaitEvent.mlx, KOAPatient\KOA4_IMUCal.mlx.